Diagram of the C-N coupled Microbial-ENzyme
Decomposition (MEND) model
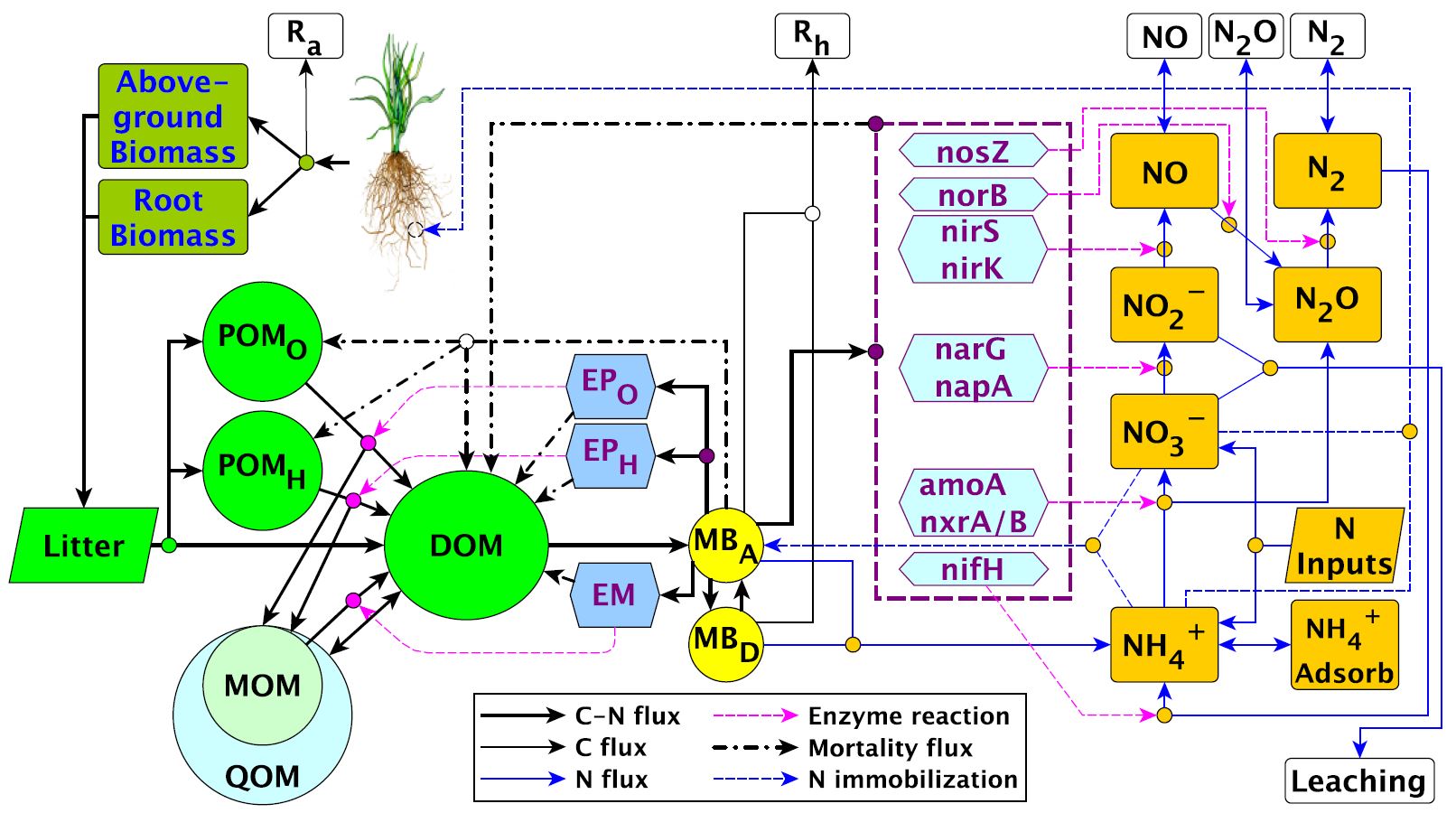 Ra
Ra and
Rh are autotrophic and
heterotrophic respiration, respectively.
POMO and
POMH are particulate organic matter (
POM)
decomposed by oxidative (
EPO) and hydrolytic
enzymes (
EPH), respectively.
MOM is
mineral-associated organic matter, which is decomposed by a mixed
enzyme group
EM. Dissolved organic matter (
DOM)
interacts with the active layer of MOM (
QOM) through sorption
and desorption.
Litter enters
POMO,
POMH, and
DOM. Microbes consist of active
(
MBA) and dormant microbes (
MBD).
DOM can be assimilated by
MBA. Mineral N deposition
and fertilization enter
NH4+ and
NO3– that can be immobilized by microbes
and taken up by plant roots. NH
4+ adsorption is
also considered. N fixation, nitrification and denitrification are
mediated by nitrogenase (
nifH), ammonia oxidases (
amoA,
nxrA/B) and N-reductases (
narG/napA,
nirS/nirK,
norB,
nosZ), respectively. Mineral N loss pathways
include leaching (NO
3– and
NO
2–) and gas emission (NO, N
2O,
and N
2) from soil to atmosphere.
 Ra and Rh are autotrophic and
heterotrophic respiration, respectively. POMO and
POMH are particulate organic matter (POM)
decomposed by oxidative (EPO) and hydrolytic
enzymes (EPH), respectively. MOM is
mineral-associated organic matter, which is decomposed by a mixed
enzyme group EM. Dissolved organic matter (DOM)
interacts with the active layer of MOM (QOM) through sorption
and desorption. Litter enters POMO,
POMH, and DOM. Microbes consist of active
(MBA) and dormant microbes (MBD).
DOM can be assimilated by MBA. Mineral N deposition
and fertilization enter NH4+ and
NO3– that can be immobilized by microbes
and taken up by plant roots. NH4+ adsorption is
also considered. N fixation, nitrification and denitrification are
mediated by nitrogenase (nifH), ammonia oxidases (amoA,
nxrA/B) and N-reductases (narG/napA, nirS/nirK,
norB, nosZ), respectively. Mineral N loss pathways
include leaching (NO3– and
NO2–) and gas emission (NO, N2O,
and N2) from soil to atmosphere.
Ra and Rh are autotrophic and
heterotrophic respiration, respectively. POMO and
POMH are particulate organic matter (POM)
decomposed by oxidative (EPO) and hydrolytic
enzymes (EPH), respectively. MOM is
mineral-associated organic matter, which is decomposed by a mixed
enzyme group EM. Dissolved organic matter (DOM)
interacts with the active layer of MOM (QOM) through sorption
and desorption. Litter enters POMO,
POMH, and DOM. Microbes consist of active
(MBA) and dormant microbes (MBD).
DOM can be assimilated by MBA. Mineral N deposition
and fertilization enter NH4+ and
NO3– that can be immobilized by microbes
and taken up by plant roots. NH4+ adsorption is
also considered. N fixation, nitrification and denitrification are
mediated by nitrogenase (nifH), ammonia oxidases (amoA,
nxrA/B) and N-reductases (narG/napA, nirS/nirK,
norB, nosZ), respectively. Mineral N loss pathways
include leaching (NO3– and
NO2–) and gas emission (NO, N2O,
and N2) from soil to atmosphere.

